A Comprehensive Guide to Electric Cars and Their Pros and Cons
 |
| pros and cons electric car |
With the rising global concern over emissions and climate change, electric cars are becoming a more popular choice for those looking to buy a vehicle with reduced environmental impact.
But before making a big purchase decision like this, it's important to understand both the pros and cons of electric cars. In this guide, we'll explore the advantages and disadvantages of hybrid and battery-electric vehicles.
Definition Electric Cars
Electric cars, also known as electric vehicles (EVs), are automobiles that are powered by one or more electric motors and use energy stored in a battery to operate.
They can be charged from an external source and do not require gasoline to run. EVs can either be fully or partially powered by electricity, and they have low emissions compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Unlike traditional gasoline-powered cars, electric cars are powered by an electric motor that runs on a rechargeable battery. The battery can be charged by plugging the car into an electrical socket or charging station, making it a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative to gas-powered cars.
How do Electric Cars Work?
 |
| electric car work |
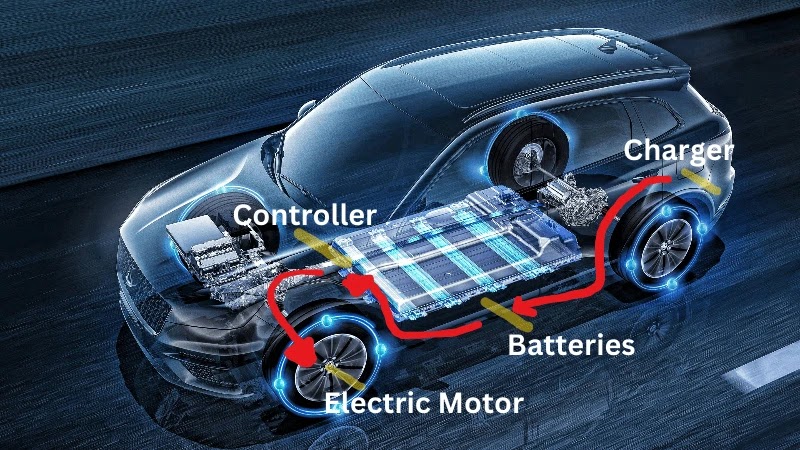
Electric cars work by converting stored energy in the battery into mechanical energy that powers the car's wheels.
Electrical parts work together to make this move happen. The car must be plugged into a wall outlet or charging equipment to recharge the battery pack.
The battery provides electricity to the car's motor, which then turns the wheels. The process is simple and efficient, producing no exhaust emissions and reducing carbon footprint.
Types of Electric Cars
When it comes to electric cars, there are a few different types to choose from. In this section, we'll take a closer look at the three main types: hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and battery-electric vehicles (BEVs).
1. Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are a type of vehicle that combines an internal combustion engine with one or more electric motors.
Electricity and gasoline: the perfect pair powering Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)! The electric motor is powered by a battery that is charged by the gasoline engine and regenerative braking.
The electric motor is powered by energy stored in a battery, and it works together with the internal combustion engine to propel the vehicle. HEVs are different from plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), which can be charged from an external power source.
HEVs are designed to switch between the two power sources depending on the driving situation. For example, the gasoline engine may kick in when accelerating or climbing hills, while the electric motor may be used for low-speed cruising.
2. Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) are a type of hybrid electric vehicle that uses batteries to power an electric motor, as well as another fuel such as gasoline or diesel to power an internal combustion engine.
PHEVs have an electric range that is usually longer than conventional hybrids, but shorter than pure EVs. They can be recharged by plugging a charging cable into an external power source.
3. Battery-electric Vehicles (BEVs)
Battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) are a type of electric vehicle that uses a battery pack to store electrical energy that powers the motor. They are powered by rechargeable lithium-ion batteries and operate only on stored electricity.
BEVs have one or more electric motors and are fairly simple and easy to operate compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
Pros and Cons
What are the pros of electric cars?
Electric cars have become increasingly popular in recent years as more people look for greener and more sustainable modes of transportation. In this comprehensive guide, we will take a closer look at the pros and cons of electric cars to help you make an informed decision if you are considering purchasing one.
Low Maintenance: One of the most significant advantages of owning an electric car is that they require less maintenance than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. Because electric cars have fewer moving parts, there is less wear and tear on the vehicle.
Zero Emissions: Another significant advantage of electric cars is that they produce zero emissions. Unlike gas-powered vehicles, electric cars do not emit harmful pollutants into the environment, such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter.
Quieter Driving Experience: Electric cars are also quieter than gasoline-powered vehicles, which makes them a more pleasant driving experience. The electric motor produces significantly less noise than a gas engine, resulting in a smoother and more peaceful ride. This can be especially beneficial when driving in urban areas or residential neighbourhoods.
Government Incentives: Electric cars often come with government incentives, such as tax credits or rebates, which can help offset the cost of purchasing an electric car. These incentives vary depending on your location, but they can be a significant factor in making electric cars more affordable for consumers.
Cons of Electric Cars
High Upfront Cost: The price is a major drawback for people looking to purchase an electric car. Electric cars have a long way to go before they become mainstream. Whether we’re ready for it or not, the electric car is making its mark in history. But electric cars aren't new, and they certainly aren't perfect.
Limited Range on a Single Charge: Electric cars use lithium-ion batteries, these cells give an electric car more than 200 miles on a single charge. Other problems include running out of power in the middle of a trip and waiting for hours to recharge the battery. As a result, electric cars have a limited range, making long trips difficult.
Long Recharging Time: There is a minimum time you will have to wait after your electric car battery dies out. You will have to wait till the battery gets fully recharged. An average electric vehicle takes around 8 hours to recharge completely.
Potential Diminished Performance in Cold Weather: The acceleration of an electric car can feel less zippy in cold weather.
The difficulty of Replacing Batteries: For vehicles with only 150,000 km, battery replacement can be more expensive than the car's value. No matter what steps you take to prolong battery life, eventually its capacity will dwindle and it will cease to work. With an Electric Vehicle battery, you can expect around ten years of reliable performance.
Advantages of Electric Vehicles
Electric cars have clear advantages over their traditional gasoline-powered counterparts, offering a range of benefits. Electric cars are more energy efficient, meaning they convert more of the energy from their fuel source into actual energy.
Electric cars have lower emissions and carbon footprints, reducing their impact on the environment. Electric cars perform well and require less maintenance than traditional gas-powered vehicles.
Electric Vehicles are quieter than gasoline-powered cars, making them more comfortable to drive. Another advantage of electric cars is that they are cost-effective in the long run.
Disadvantages of Electric Cars
 |
| electric cars disadvantages |
Despite their many benefits, electric cars also have some drawbacks. One of the most significant disadvantages is their limited driving range. Most EVs can only travel for up to 200-300 miles on a single charge, which may not be enough for long-distance travel. Additionally, charging infrastructure is still developing, which means finding charging stations can be challenging.
Electric cars are a promising alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. They are eco-friendly, cost-effective, and quiet. While they have some limitations, such as limited driving range and charging infrastructure, these issues are being addressed by manufacturers and governments worldwide. By choosing an electric car, you can contribute to a greener future while enjoying the benefits of modern technology.
Are Electric Vehicles Worth It?
While electric vehicles offer many benefits, they also have some drawbacks. For example, battery charging can take a long time, which may not fit everyone's driving needs. Additionally, electric cars tend to be more expensive upfront, making them a larger investment. Ultimately, it is up to the driver to decide if an electric car is the right fit for them and their lifestyle.
Electric cars are skyrocketing in popularity, thanks to the multitude of advantages they bring to the table. However, they also have some drawbacks, including higher upfront costs and longer charging times. Before purchasing an electric car, it's important to weigh the pros and cons carefully and determine if this type of vehicle is the right fit for you.
What is the downside of an electric car?
One of the main downsides of electric cars is their range. The range of an electric car is limited by the battery capacity.
Another downside of electric cars is the cost of charging. Charging an electric car can be more expensive than fueling a gas-powered car.
Electric cars also have longer charging times than gas-powered vehicles. This can be inconvenient for long trips.
What is the biggest problem with electric cars?
One of the biggest problems with electric cars is their limited range. The limited range of electric cars is a result of their reliance on batteries.
Most electric cars can only travel between 100-200 miles on a single charge. This makes them unsuitable for long-distance trips, as you would need to recharge them frequently.
The charging infrastructure is not yet fully developed, so finding a charging station can be difficult in some areas.
Pros and Cons of Electric Cars Scholarly Articles
Electric cars have seen a surge in popularity over the past few years, thanks to their numerous benefits over petrol-powered vehicles. However, it is important to consider both the pros and cons of electric cars before making a decision about which type of vehicle to purchase. Scholarly articles can provide valuable research on the advantages and disadvantages of electric cars, helping you make an informed decision.
Hybrid Electric Vehicle
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are an innovative and eco-friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. They combine the benefits of both conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and electric vehicles (EVs). In this section, we will explore the definition and components of a hybrid electric vehicle, as well as discuss the different types of HEVs available in the market.
Components of a Hybrid Electric Vehicle
A typical HEV consists of the following main components:
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE): This is the conventional gasoline-powered engine that is found in most traditional vehicles. The ICE in HEVs is usually smaller and more fuel-efficient compared to those in non-hybrid vehicles.
Electric Motor: The electric motor in a hybrid vehicle works alongside the ICE to provide additional power when needed, such as during acceleration or hill climbing. This allows the vehicle to use less gasoline and produce fewer emissions.
Battery: The battery in an HEV stores electric energy generated by the vehicle's regenerative braking system and the ICE. This stored energy is then used to power the electric motor when needed.
Regenerative Braking System: This system converts the vehicle's kinetic energy into electrical energy during deceleration, which is then stored in the battery. This reduces the need for the vehicle to rely solely on its ICE for power, thus improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
Start-Stop System: Many HEVs are equipped with a start-stop system that shuts down the ICE when the vehicle is idling, such as at a stoplight, and restarts it when needed. This helps reduce idle emissions and further improve fuel efficiency.
Types of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
There are several types of HEVs available in the market, each with varying degrees of reliance on electric power:
Series Hybrid: In this type of HEV, the ICE is used solely to generate electricity, which powers the electric motor that drives the vehicle. The ICE (Internal Combustion Engine) is not the one turning the wheels - it's the power behind them. This configuration allows the ICE to operate at its most efficient speed, improving overall fuel economy.
Parallel Hybrid: In a parallel hybrid, both the ICE and the electric motor can power the vehicle independently or together. This allows the vehicle to switch seamlessly between gasoline and electric power, depending on driving conditions and battery charge level.
Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV): A PHEV is a type of hybrid that can be plugged into an external power source to recharge its battery, in addition to charging through regenerative braking and the ICE. This allows the vehicle to have a larger all-electric range compared to conventional hybrids while still maintaining
Pros and Cons of Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid vehicles are becoming increasingly popular as people seek to reduce their carbon footprint and save money on gas. However, before you decide to purchase a hybrid vehicle, it's important to understand the pros and cons. In this section, we'll take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of hybrid vehicles.
Pros:
Fuel efficiency: One of the main advantages of hybrid vehicles is their fuel efficiency. Since they combine a gasoline engine with an electric motor, they require less gasoline to run than traditional gasoline-powered cars. By saving money on gas, you can not only be thrifty, but you can also help to lower your carbon footprint!
Regenerative braking: Hybrid vehicles also use regenerative braking to recharge their batteries. When you brake, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting the kinetic energy into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This means that you don't have to rely solely on gasoline to power your car.
Lower emissions: Since hybrid vehicles use less gasoline, they also produce fewer emissions than traditional cars. This is good news for the environment and can help to reduce your carbon footprint.
Cons:
Cost: One of the main downsides of hybrid vehicles is that they can be more expensive than traditional cars. While you may save money on gas in the long run, you'll have to pay more upfront to purchase a hybrid vehicle.
Performance: Another potential downside of hybrid vehicles is that they may not be as powerful as gasoline-powered cars. While this isn't always an issue, it could be a factor for some drivers who value speed and acceleration.
Battery life: Hybrid vehicles rely on batteries to power their electric motors, and these batteries can degrade over time. This means that you may need to replace the batteries at some point, which can be expensive.
Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle
A PHEV is an innovative type of vehicle that combines the fuel efficiency of an electric motor and the convenience of a gasoline-powered engine. This means that PHEVs can run on electricity from a rechargeable battery, as well as gasoline.
The benefit of a PHEV is that it allows you to drive using pure electric power for short distances. This makes them ideal for city driving, where the ability to switch between electric and gas power provides greater range flexibility.
For longer trips, the gasoline engine can take over, providing extended range without the need for frequent charging.
Pros and Cons of Plug-In Hybrids
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) have emerged as a popular alternative for environmentally conscious drivers who want to reduce their carbon footprint without sacrificing convenience. In this section, we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of plug-in hybrid vehicles and provide insights to help you determine if a PHEV is right for you.
Pros:
Extended Electric Range: One of the most significant benefits of owning a PHEV is its extended electric range compared to traditional hybrid vehicles. With a larger battery capacity, PHEVs can cover greater distances on electric power alone, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
Reduced Fuel Costs and Emissions: By maximizing the use of electric power, PHEV owners can save money on fuel costs and reduce their overall emissions. This makes PHEVs an attractive option for those looking to minimize their environmental impact and cut down on expenses associated with gasoline consumption.
Flexibility and Convenience: PHEVs offer the best of both worlds when it comes to power sources. When the battery is depleted, the internal combustion engine kicks in, providing a seamless transition between electric and gasoline power. This ensures that drivers never have to worry about running out of charge or finding a charging station during long trips.
Tax Incentives and Rebates: In many countries, including the United States, PHEV buyers can benefit from tax incentives and rebates designed to encourage the adoption of eco-friendly vehicles. These financial benefits can help offset the initial cost of purchasing a PHEV and make them more affordable for consumers.
Cons:
PHEVs cost about $1,000 to $3,000 more than comparable gas-only vehicles. The initial cost of a PHEV is higher because it incorporates both an electric motor and a gasoline engine.
PHEVs are more complex than gas-only vehicles and have more parts that can break. Although electric motors and batteries offer very low failure rates, fixing a two-part drivetrain could be expensive.
Plug-in components often take up cargo space in PHEVs. This means that the cargo capacity of a PHEV may be less than that of a comparable gas-only vehicle.
Charging can be challenging for PHEVs: Although some plug-ins can go 25 miles or more on pure electric power without burning any fuel. Charging times for these batteries are about 5.5 hours using 120-volt household current and about two hours on a 240-volt charger.
What are 3 Disadvantages of Electric Cars
As electric cars become more popular and mainstream, it's essential to understand not only their benefits but also some of the drawbacks associated with them. There are three significant disadvantages of electric cars: limited driving range, long recharging times, and higher upfront costs.
Limited Driving Range. One of the primary concerns for potential electric car buyers is the limited driving range compared to gas-powered vehicles. On average, electric cars have a shorter range than their gasoline counterparts.
Long Recharging Times. Another significant disadvantage of electric cars is the time it takes to recharge their batteries. Unlike filling up a gas tank, which takes just a few minutes, recharging an electric car battery can be a much more time-consuming process. With Level 1 or Level 2 chargers, it can take up to eighty hours to fully recharge a battery pack. Even fast-charging stations, which are becoming more common, still require about 30 minutes to charge an electric car battery to 80% capacity. This means that electric car drivers need to plan their trips more carefully, as running out of power can't be solved by a quick stop at a gas station.
Higher Upfront Costs. While electric cars can save drivers money in the long run due to lower fuel and maintenance costs, the initial price tag for these vehicles is usually higher than that of comparable gas-powered cars. Although battery packs in electric vehicles are more expensive, they tend to last a long time and often come with 8-10 year warranties. Additionally, federal and state incentives are available to help reduce the initial purchase price of electric cars. However, the higher upfront cost can still be a barrier for some potential buyers.
Battery-Electric Vehicles
Battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) are cars that run solely on electricity stored in a battery pack, which powers one or more electric motors.
BEVs can be charged almost anywhere and usually at a much lower cost than fueling with gasoline. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in BEVs.
These vehicles do not use any gasoline, making them environmentally friendly. All of their power is sourced solely from the battery, never needing an additional engine to get going.
Pros and Cons of Battery-Electric Vehicles
Electric cars have been gaining popularity in recent years, as more and more people are considering the switch to a more environmentally friendly mode of transportation. One critical decision that potential buyers must make is whether to go for a battery-electric vehicle (BEV) or a hybrid option. In this section, we will discuss the pros and cons of battery-electric vehicles, helping you make an informed decision.
Pros:
Zero Tailpipe Emissions: One of the most significant advantages of BEVs is that they produce zero tailpipe emissions. This means they do not contribute to air pollution, providing a cleaner environment and better air quality.
Lower Operating Costs: BEVs generally have lower operating costs compared to their gasoline counterparts. Electricity is often cheaper than gasoline, and electric vehicles require less maintenance as they have fewer moving parts.
Quiet Operation: Electric vehicles are known for their smooth and quiet operation, which contributes to a more enjoyable driving experience and reduced noise pollution.
Instant Torque: BEVs offer instant torque, providing quick acceleration and a responsive driving experience.
Incentives and Rebates: Many governments offer incentives and rebates to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles, making them more affordable for buyers.
Cons:
Limited Range: One of the primary downsides to electric vehicles is their limited range compared to gasoline cars. While advancements in technology are increasing the range of some electric vehicles, they still typically fall short of the distance that can be covered by a conventional gasoline car on a full tank.
Charging Infrastructure: Although the charging infrastructure for electric vehicles is improving, it is still not as widespread as gas stations. This can make long trips and road trips more challenging, as you may need to plan your route around available charging stations.
Charging Time: Charging times for electric vehicles can vary depending on the type of charger used; however, they are generally longer than the time it takes to refuel a gasoline car. This can be inconvenient, especially during long trips.
Higher Upfront Cost: While the operating costs of electric vehicles are lower, their upfront costs can be higher due to the cost of batteries and other components. However, this can be offset by the lower ongoing expenses and various incentives available.
Dependence on Rare Metals: The production of batteries for electric vehicles requires rare metals, which can have environmental and social consequences if not sourced responsibly.
Pros and Cons of Electric Cars vs Gas Cars
When it comes to making a decision between purchasing an electric car or a gas car, it is essential to weigh the pros and cons of each. In this section, we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of electric cars compared to gas cars in various aspects.
1. Maintenance and Lifetime Cost
Electric Car Pros:
- Less frequent trips to the mechanic, resulting in lower maintenance costs
- Lower lifetime cost due to fewer parts needing replacement
Gas Car Cons:
- Regular maintenance, such as oil changes, coolant, and transmission fluid replacements, can add up over time
- Higher lifetime cost due to more frequent maintenance requirements
2. Environmental Impact
Electric Car Pros:
- Zero tailpipe emissions
- Not directly powered by fossil fuels
Gas Car Cons:
- Contribute to pollution and toxic waste due to exhaust emissions and non-biodegradable waste from oil and fluids.
3. Charging and Driving Range
Electric Car Cons:
- Fewer charging stations compared to gas stations
- Longer charging times
- Limited driving range on a full charge
Gas Car Pros:
- More accessible fueling stations
- Quicker refueling process
- Generally longer driving range on a full tank
Pros and Cons of Electric Cars on the Environment
Electric cars have become increasingly popular in recent years, promising a more sustainable and eco-friendly mode of transportation. While they offer several advantages over traditional gasoline-fueled vehicles, there are also some drawbacks to consider. In this section, we will explore the pros and cons of electric cars on the environment.
Pros:
Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Electric vehicles (EVs) produce zero tailpipe emissions, which significantly reduces their overall carbon footprint. Research indicates that EVs generally generate lower levels of greenhouse gases than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. As more renewable energy sources like wind and solar are utilized for electricity generation, the overall environmental impact of EVs will continue to decrease.
Improved air quality: Since electric cars do not emit exhaust fumes, they contribute to better air quality in urban areas. This is particularly important for individuals who live in cities with high levels of air pollution, as it can help reduce associated respiratory health issues.
Encouragement of renewable energy: The increasing demand for electric cars has spurred greater investment in renewable energy technologies. As a result, countries and utility companies are working to transition from fossil fuels to cleaner sources of power, such as wind and solar.
Cons:
Particulate matter pollution: Despite producing no tailpipe emissions, EVs still contribute to particulate matter pollution due to brake dust, airborne road dust, and tire erosion. These particles can be harmful to respiratory health, particularly for those living in densely populated areas.
Battery production and disposal: The production of batteries for electric cars requires significant amounts of energy and raw materials, which can have negative environmental impacts. Furthermore, proper disposal and recycling of used batteries remain a challenge, with potential risks of toxic waste leakage.
Dependence on electricity generation: The overall environmental impact of an electric car depends largely on how the electricity is used to charge.

Post a Comment for "A Comprehensive Guide to Electric Cars and Their Pros and Cons"